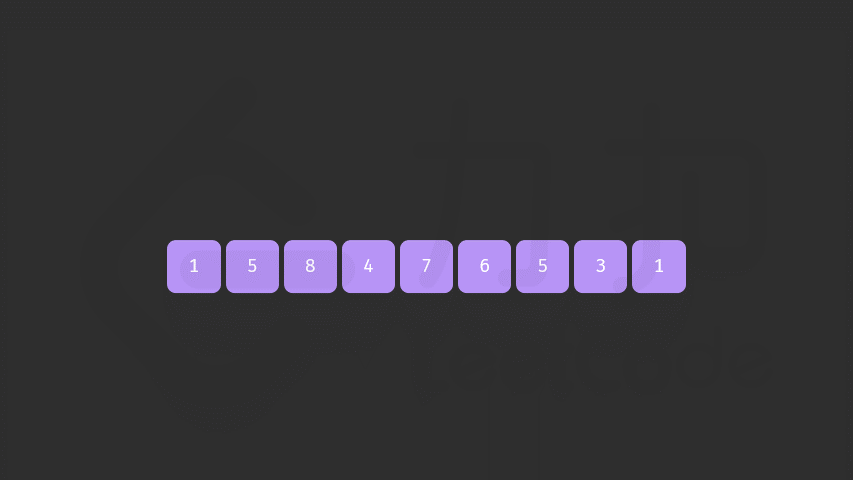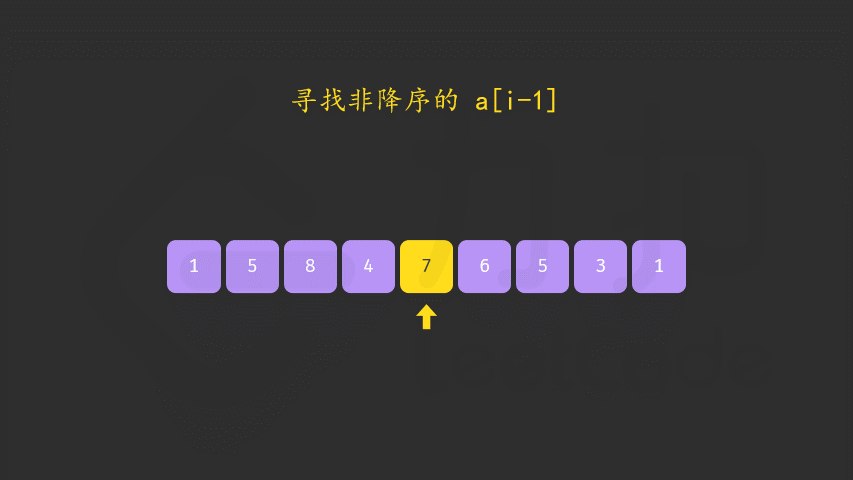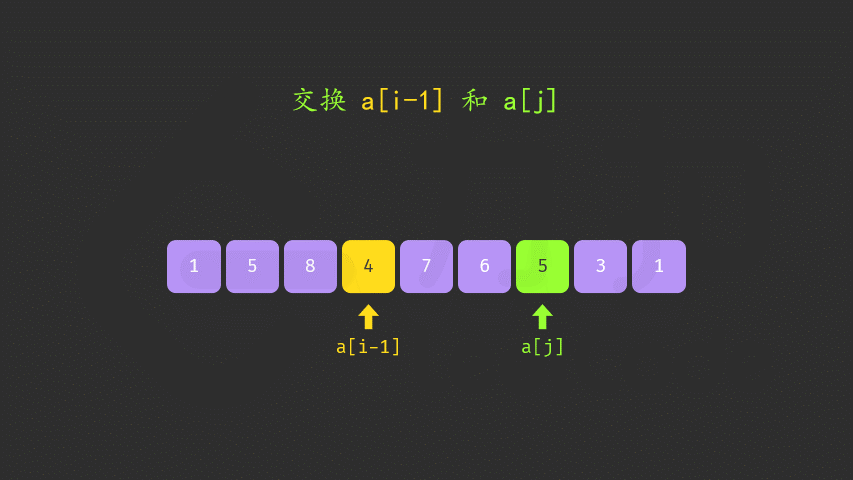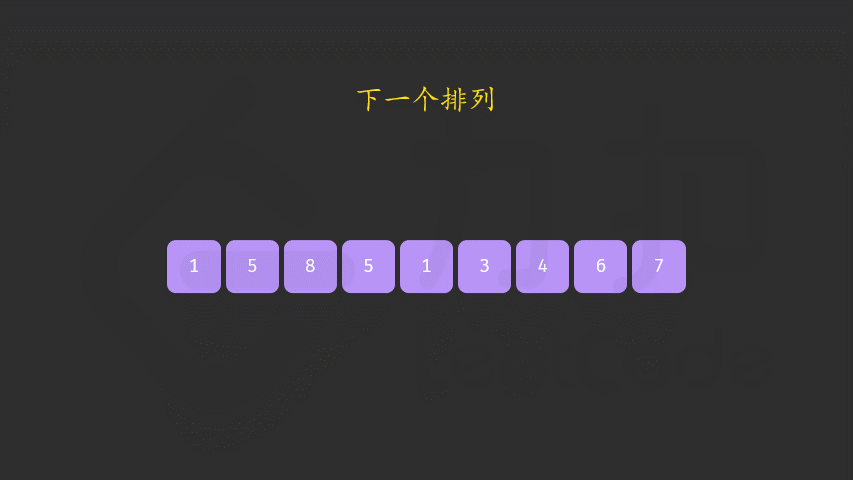排序 思想是归并排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null )return head; ListNode fast = head.next, slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode tmp = slow.next; slow.next = null ; ListNode left = sortList(head); ListNode right = sortList(tmp); ListNode h = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode res = h; while (left != null && right != null ){ if (left.val < right.val){ h.next = left; left = left.next; }else { h.next = right; right = right.next; } h = h.next; } h.next = left != null ? left : right; return res.next; }
这道题首先需要给数组排序, 按照x[0]排好位置,然后分为两种情况:
1.链表没有数据并且当前数组[0] 《= 前一个数组[1],那这样就要更新数据,判断前一个数组[1]是否需要更新数据
2.直接添加数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { ArrayList<int []> res = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(intervals,(x, y) -> x[0 ] - y[0 ]); for (int []p : intervals){ int m = res.size(); if (m > 0 && p[0 ] <= res.get(m - 1 )[1 ]){ res.get(m - 1 )[1 ] = Math.max(res.get(m - 1 )[1 ],p[1 ]); }else { res.add(p); } } return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][]); }
**
这道题看题目可知,他需要返回原数组,所以不需要构建新数组或者链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public int removeElement (int [] nums, int val) { Arrays.sort(nums); int j = 0 ; for (int i : nums){ if (i != val){ nums[j] = i; j++; } } return j; }
这道题也可以套用快排模板的,主要是比较每一个 str 的大小,所以需要使用到compareTo函数。思路如下:、
若拼接字符串 x + y > y + x ,则 x “大于” y 。 反之,若 x + y < y + x ,则 x “小于” y 。
在 Java 中, <font style="color:rgba(6, 8, 31, 0.88);">compareTo</font> 方法是 <font style="color:rgba(6, 8, 31, 0.88);">Comparable</font> 接口的一部分,用于比较两个对象。其返回值的含义如下:
如果返回值小于 0,表示调用该方法的对象在字典顺序上小于被比较的对象。 如果返回值等于 0,表示两个对象相等。 如果返回值大于 0,表示调用该方法的对象在字典顺序上大于被比较的对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public String largestNumber (int [] nums) { String[] strs = new String [nums.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ strs[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]); } Arrays.sort(strs, (x , y) -> (x + y).compareTo(y + x)); StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder (); if (strs[strs.length - 1 ].equals("0" ))return "0" ; for (int i = strs.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ res.append(strs[i]); } return res.toString(); } public void sort (String strs[], int l, int r) { if (l >= r)return ; int i = l - 1 , j = r + 1 ; String x = strs[l]; while (i < j){ do i++; while ((strs[i] + x).compareTo(x + strs[i]) < 0 ); do j--; while ((strs[j] + x).compareTo(x + strs[j]) > 0 ); if (i < j){ String tmp = strs[i]; strs[i] = strs[j]; strs[j] = tmp; } } sort(strs, l, j); sort(strs, j + 1 , r); }
这里有两种做法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Arrays.sort(strs, (x , y) -> (x + y).compareTo(y + x)); public void sort (String strs[], int l, int r) { if (l >= r)return ; int i = l - 1 , j = r + 1 ; String x = strs[l]; while (i < j){ do i++; while ((strs[i] + x).compareTo(x + strs[i]) < 0 ); do j--; while ((strs[j] + x).compareTo(x + strs[j]) > 0 ); if (i < j){ String tmp = strs[i]; strs[i] = strs[j]; strs[j] = tmp; } } sort(strs, l, j); sort(strs, j + 1 , r); }
快排只需要修改while里面的判定条件即可。
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">n</font> 个元素的数组 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">nums</font> , 原地 对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
其实就是快排,把模板放上去即可!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public void sortColors (int [] nums) { sort(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } public void sort (int [] nums, int l, int r) { if (l >= r)return ; int i = l - 1 , j = r + 1 , x = nums[l]; while (i < j){ do i++; while (nums[i] < x); do j--; while (nums[j] > x); if (i < j){ int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } } sort(nums, l, j); sort(nums, j + 1 , r); }
快排的另一种变形,快速选择。主要是利用排序后查找某个特定元素。
基本思路与「快速排序」一致,每次敲定一个基准值 x,根据当前与 x 的大小关系,将范围在 [l,r] 的 nums[i] 划分为到两边。
同时利用,利用题目只要求输出第 k 大的值,而不需要对数组进行整体排序,我们只需要根据划分两边后,第 k 大数会落在哪一边,来决定对哪边进行递归处理即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { return sort(nums,0 ,nums.length - 1 , nums.length - k ); } public int sort (int nums[], int l , int r, int k) { if (l >= r)return nums[k]; int i = l - 1 , j = r + 1 , x = nums[l]; while (i < j){ do i++; while (nums[i] < x); do j--; while (nums[j] > x); if (i < j){ int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } } if (k <= j)return sort(nums, l , j , k); else return sort(nums,j + 1 ,r, k); }
目前只会简单暴力法
如果数组长度为奇数,中位数就等于中间数 , 否则, 等于 中间两个数之和 / 2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public double findMedianSortedArrays (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int []nums = new int [nums1.length + nums2.length]; int i = 0 ; for (; i < nums1.length; i++){ nums[i] = nums1[i]; } for (int j : nums2){ nums[i++] = j; } Arrays.sort(nums); return (nums[(nums.length - 1 )/ 2 ] + nums[(nums.length / 2 )]) / 2.0 ; }
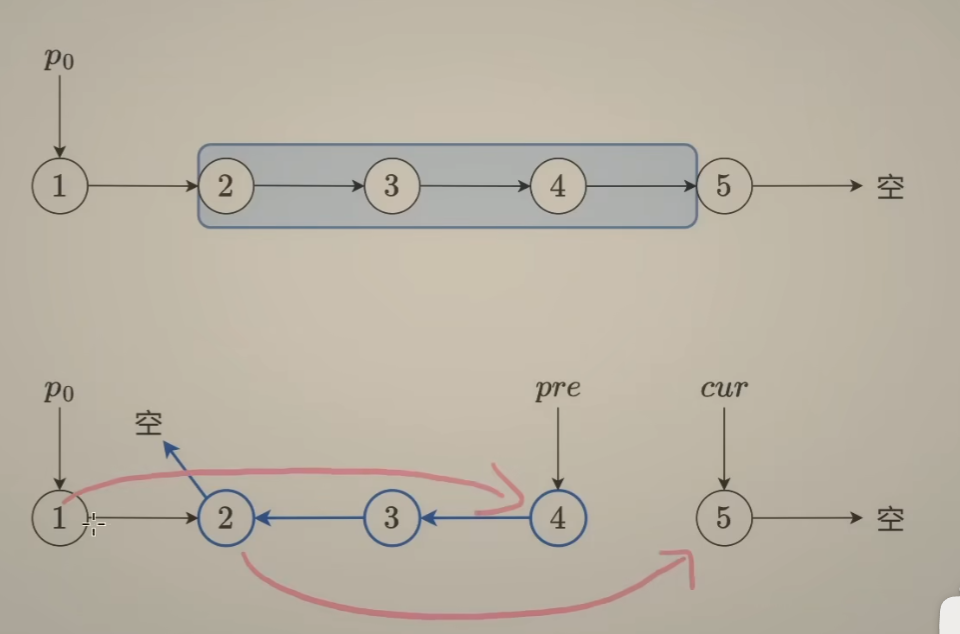
链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode p = head; ListNode q = null ; while (p != null ){ ListNode tmp = p.next; p.next = q; q = p; p = tmp; } return q; }
利用双指针修改链表的方向
注意这里的索引是从 1 开始的。 迭代的思路大概是:先用一个 for 循环找到第 m 个位置,然后再用一个 for 循环将 m 和 n 之间的元素反转。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int left, int right) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode p = dummy; for (int i = 0 ; i < left - 1 ; i++) p = p.next; ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = p.next; for (int i = 0 ; i < right - left + 1 ; i++){ ListNode tmp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = tmp; } p.next.next = cur; p.next = pre; return dummy.next; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public ListNode middleNode (ListNode head) { ListNode p = head; ListNode q = head; while (q != null && q.next != null ){ q = q.next.next; p = p.next; } return p; }
也是双指针,只是需要注意while()里面的判定条件
设「第一个公共节点」为 node ,「链表 headA」的节点数量为 a ,「链表 headB」的节点数量为 b ,「两链表的公共尾部」的节点数量为 c ,则有:
头节点 headA 到 node 前,共有 a−c 个节点;
头节点 headB 到 node 前,共有 b−c 个节点;
考虑构建两个节点指针 A , B 分别指向两链表头节点 headA , headB ,做如下操作:
指针 A 先遍历完链表 headA ,再开始遍历链表 headB ,当走到 node 时,共走步数为:a+(b−c)
指针 B 先遍历完链表 headB ,再开始遍历链表 headA ,当走到 node 时,共走步数为:b+(a−c)
如下式所示,此时指针 A , B 重合,并有两种情况:
a+(b−c)=b+(a−c)
若两链表 有 公共尾部 (即 c>0 ) :指针 A , B 同时指向 [第一个公共节点] node 。
若两链表 无 公共尾部 (即 c=0 ) :指针 A , B 同时指向 null 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode a = headA; ListNode b = headB; while (a != b){ a = a == null ? headB : a.next; b = b == null ? headA : b.next; } return a; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (slow == fast) return true ; } return false ; }
分成快慢指针,一个指着偶数,一个奇数,快的为奇数。
遍历:
慢指针的下一个指向快指针的下一个(即使偶数)
快指针的下一个指向满指针的下一个(即使奇数)
最后把两个链表拼接起来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public ListNode oddEvenList (ListNode head) { if (head == null )return null ; ListNode fast = head.next; ListNode slow = head; ListNode dummyFast = fast; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ slow.next = fast.next; slow = slow.next; fast.next = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } slow.next = dummyFast; return head; }
队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 private LinkedList<Integer> list = null ; public MyStack () { list = new LinkedList <>(); } public void push (int x) { list.addLast(x); } public int pop () { if (empty()){ return -1 ; }else { return list.remove(list.size() - 1 ); } } public int top () { return list.get(list.size() - 1 ); } public boolean empty () { return list.size() == 0 ; }
空值处理: 当 matrix 为空时,直接返回空列表 [] 即可。
初始化: 矩阵 左、右、上、下 四个边界 l , r , t , b ,用于打印的结果列表 res 。
循环打印: “从左向右、从上向下、从右向左、从下向上” 四个方向循环打印。
根据边界打印,即将元素按顺序添加至列表 res 尾部。
边界向内收缩 1 (代表已被打印)。
判断边界是否相遇(是否打印完毕),若打印完毕则跳出。
返回值: 返回 res 即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) { if (matrix.length == 0 )return new ArrayList <Integer>(); int l = 0 , r = matrix[0 ].length - 1 , t =0 , b = matrix.length - 1 , x =0 ; Integer[] res = new Integer [(r +1 ) * (b + 1 )]; while (true ){ for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)res[x++] = matrix[t][i]; if (++t > b)break ; for (int i = t; i <= b; i++)res[x++] = matrix[i][r]; if (--r < l)break ; for (int i = r; i >= l; i--)res[x++] = matrix[b][i]; if (--b < t)break ; for (int i = b; i >= t; i--)res[x++] = matrix[i][l]; if (++l > r)break ; } return Arrays.asList(res); }
栈 当调用 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">push</font> 让元素入队时,只要把元素压入 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">s1</font> 即可,时间复杂度 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">O(1)</font>:
使用 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">peek</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">pop</font> 操作队头的元素时,若 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">s2</font> 为空,可以把 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">s1</font> 的所有元素取出再添加进 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">s2</font>, 这时候 **<font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">s2</font>** 中元素就是先进先出顺序了 ,不过这样移动所有元素的复杂度是 <font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">O(n)</font>:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class MyQueue { Stack<Integer> stack1; Stack<Integer> stack2; public MyQueue () { stack1 = new Stack <>(); stack2 = new Stack <>(); } public void push (int x) { stack1.push(x); } public int pop () { peek(); return stack2.pop(); } public int peek () { if (stack2.isEmpty()){ while (!stack1.empty()){ int val = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(val); } } return stack2.peek(); } public boolean empty () { return stack2.size() == 0 && stack1.size() == 0 ; } }
每个元素入栈时,还要记下来当前栈中的最小值 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class MinStack { Stack<Integer> stack; Stack<Integer> minStack; public MinStack () { stack = new Stack <>(); minStack = new Stack <>(); } public void push (int val) { stack.push(val); if (minStack.isEmpty() || val <= minStack.peek()){ minStack.push(val); } } public void pop () { if (stack.pop().equals(minStack.peek())){ minStack.pop(); } } public int top () { return stack.peek(); } public int getMin () { return minStack.peek(); } }
利用栈存储数字,判断如果是符号,则取栈中元素出来计算。
但要判断第二个取出来元素 是/ - 于第一个元素的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public int evalRPN (String[] tokens) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (String token: tokens){ if ("+-*/" .contains(token)){ int a = stack.pop(),b = stack.pop(); switch (token){ case "+" : stack.push(a + b); break ; case "-" : stack.push(b - a); break ; case "*" : stack.push(a *b); break ; case "/" : stack.push(b / a); break ; } }else { stack.push(Integer.valueOf(token)); } } return stack.pop(); }
和上一题差不多思路,**每个右括号 **<font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">)</font>** 的左边必须有一个左括号 **<font style="color:rgb(233, 105, 0);background-color:rgb(245, 245, 245);">(</font>** 和它匹配 **。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public boolean isValid (String s) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack <>(); for (char c : s.toCharArray()){ if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c=='{' )stack.push(c); else { if (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == left(c)){ stack.pop(); }else { return false ; } } } return stack.isEmpty(); } public char left (char c) { if (c ==')' )return '(' ; else if (c == ']' )return '[' ; return '{' ; } }
双栈实现,通过一个新栈存储返回历史记录数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class BrowserHistory { Stack<String> stack1 = new Stack <>(); Stack<String> stack2 = new Stack <>(); public BrowserHistory (String homepage) { stack1.push(homepage); } public void visit (String url) { stack1.push(url); stack2.clear(); } public String back (int steps) { while (steps-- > 0 && stack1.size() > 1 ){ stack2.push(stack1.pop()); } return stack1.peek(); } public String forward (int steps) { while (steps-- > 0 && stack2.size() > 0 ){ stack1.push(stack2.pop()); } return stack1.peek(); } }
迭代字符串:
- 如果当前字符与前一个相同,栈顶元素加 1。
- 否则,往栈中压入 1。
* 如果栈顶元素等于 k,则从字符串中删除这 k 个字符,并将 k 从栈顶移除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public String removeDuplicates (String s, int k) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (s); Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < sb.length(); i++){ if (i == 0 || sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(i - 1 )){ stack.push(1 ); }else { int inc = stack.pop() + 1 ; if (inc == k){ sb.delete(i - k + 1 , i + 1 ); i = i - k; }else { stack.push(inc); } } return sb.toString(); } }
用一个ok数组记录无效括号的位置
遍历字符串
如果是( 则进入数组 并且标记为无效,因为只有一个括号而已
如果是)判断栈是否为空,
是的话则说明它是无效数组
不是的话,则找到他前一个括号的位置,标记为有效数组
然后利用StringBuilder存储数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public String minRemoveToMakeValid (String s) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); boolean [] ok = new boolean [s.length()]; StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ char c = s.charAt(i); if (c == '(' ){ stack.push(i); ok[i] = true ; } if (c == ')' ){ if (stack.isEmpty()){ ok[i] = true ; }else { ok[stack.pop()] = false ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ if (!ok[i]){ res.append(s.charAt(i)); } } return res.toString(); } }
遍历数组
设置boolean ok判断是否成功
当ok,栈不为空,并且栈顶 > 0 数组小于0
如果栈顶元素 >= 数组元素 ,就说明数组元素的行星被撞碎了;退出循环
如果栈顶元素 <= 数组元素,栈顶元素的行星被撞碎了
如果还是ok 则把行星添加进去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int [] asteroidCollision(int [] ast) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i : ast){ boolean ok = true ; while (ok && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > 0 && i < 0 ){ if (stack.peek() + i >= 0 )ok = false ; if (stack.peek() + i <= 0 )stack.pop(); } if (ok)stack.push(i); } int size = stack.size(); int [] res = new int [size]; while (!stack.isEmpty())res[--size] = stack.pop(); return res; } }
哈希 遍历数组,如果map中存在target - nums[i] 就说明
target - nums[i] 和 nums[i] 是我们要找的数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); if (nums.length < 2 )return new int []{-1 ,-1 }; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){ return new int []{i,map.get(target - nums[i])}; } map.put(nums[i],i); } return new int []{}; } }
1.将数组放进set中,去重
2.遍历set
如果set包含n - 1,说明他不是起点,continue
如果不包含,说明他是起点, 循环找出最长序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int n : nums){ set.add(n); } int res = 0 ; for (int n : set){ if (!set.contains(n - 1 )){ int num = n; int len = 1 ; while (set.contains(num + 1 )){ num += 1 ; len += 1 ; } res = Math.max(res, len); } } return res; } }
每次获取时,判断是否存在该元素,需要将数据重新放置最后的位置,标记最近使用
每次添加元素,需考虑是不是原有数据,是的话删除,重新放置
考虑容量,删除最旧最未使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class LRUCache { LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); int cap; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .cap = capacity; } public int get (int key) { if (!map.containsKey(key))return -1 ; int val = map.get(key); map.remove(key); map.put(key,val); return map.get(key); } public void put (int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)){ map.remove(key); map.put(key, value); return ; } if (map.size() >= cap){ int old = map.keySet().iterator().next(); map.remove(old); } map.put(key,value); } }
先遍历一次,找到等于0的位置
在遍历一次,把含有0的位置的行列全置0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public void setZeroes (int [][] matrix) { HashSet<Integer> set1 = new HashSet <>(); HashSet<Integer> set2 = new HashSet <>(); int m = matrix.length; int n = matrix[0 ].length; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++){ if (matrix[i][j] == 0 ){ set1.add(i); set2.add(j); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++){ if (set1.contains(i) || set2.contains(j)){ matrix[i][j] = 0 ; } } } } }
<font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">insert</font> 操作:使用哈希表判断 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">val</font> 是否存在,存在的话返回 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">false</font>,否则将其添加到 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">nums</font>,更新 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">idx</font>,同时更新哈希表; <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">remove</font> 操作:使用哈希表判断 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">val</font> 是否存在,不存在的话返回 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">false</font>,否则从哈希表中将 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">val</font> 删除,同时取出其所在 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">nums</font> 的下标 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">loc</font>,然后将 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">nums[idx]</font> 赋值到 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">loc</font> 位置,并更新 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">idx</font>( 含义为将原本处于 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">loc</font> 位置的元素删除),同时更新原本位于 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">idx</font> 位置的数在哈希表中的值为 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">loc</font>(若 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">loc</font> 与 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">idx</font> 相等,说明删除的是最后一个元素,这一步可跳过); <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">getRandom</font> 操作:由于我们人为确保了 [0, idx ] 均为存活值,因此直接在 [0, idx +1) 范围内进行随机即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class RandomizedSet { int [] nums = new int [200010 ]; HashMap<Integer, Integer> map; static int idx = -1 ; Random random = new Random (); public RandomizedSet () { map = new HashMap <>(); } public boolean insert (int val) { if (!map.containsKey(val)){ map.put(val, ++idx); nums[idx] = val; return true ; } return false ; } public boolean remove (int val) { if (map.containsKey(val)){ int loc= map.remove(val); if (loc != idx)map.put(nums[idx], loc); nums[loc] = nums[idx--]; return true ; } return false ; } public int getRandom () { return nums[random.nextInt(idx +1 )]; } }
1.首先判断最大数组,重新进入函数,减少哈希空间
2.遍历最大数组,计算每个元素的count值
3.遍历小数组,发现是否出现相同元素
如果count >0 则存在相同,count - 1,添加元素进入临时输入
如果还大于1, 修改count值
不是的话,删除该元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int [] intersect(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { if (nums1.length < nums2.length){ intersect(nums2, nums1); } Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int num : nums1){ int count = map.getOrDefault(num, 0 ) + 1 ; map.put(num, count); } int [] innums = new int [nums1.length]; int idx = 0 ; for (int num : nums2){ int count = map.getOrDefault(num, 0 ); if (count > 0 ){ count--; innums[idx++] = num; if (count > 0 ){ map.put(num, count); }else { map.remove(num); } } } return Arrays.copyOfRange(innums, 0 , idx); } }
map的value存的是对应单词的所有类型
遍历strs,对每个单词进行排序获得最简单的单词,找到存在map里的链表,如果没有则创建新的链表,然后把原来的strs存入链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) { HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap <>(); for (String s : strs){ char [] c = s.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(c); String t = String.valueOf(c); map.putIfAbsent(t,new ArrayList <>()); map.get(t).add(s); } return new ArrayList <>(map.values()); } }
二分 先遍历左边界,并且判断是否和target一致,不一致则返回-1
再遍历左边界。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { if (nums.length == 0 )return new int []{-1 ,-1 }; int i = searchL(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 , target); if (i == -1 )return new int []{-1 ,-1 }; int j = searchR(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ,target); return new int []{i,j}; } public int searchL (int [] nums, int l , int r, int target) { while (l < r){ int mid = l + (r - l ) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] < target){ l = mid + 1 ; }else { r = mid; } } if (nums[l] == target)return l; return -1 ; } public int searchR (int [] nums, int l , int r, int target) { while (l < r){ int mid = l + (r - l + 1 ) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] > target){ r = mid - 1 ; }else { l = mid; } } return l; } }
设 x=nums[mid] 是我们现在二分取到的数。
现在需要判断 x 和 target 的位置关系,谁在左边,谁在右边?
核心思路
如果 x 和 target 在不同的递增段:
如果 target 在第一段(左),x 在第二段(右),说明 x 在 target 右边;
如果 target 在第二段(右),x 在第一段(左),说明 x 在 target 左边。
如果 x 和 target 在相同的递增段:比较 x 和 target 的大小即可。
下面只讨论 x 在 target 右边,或者等于 target 的情况。其余情况 x 一定在 target 左边。
如果 x>nums[n−1],说明 x 在第一段中,那么 target 也必须在第一段中(否则 x 一定在 target 左边)且 x 必须大于等于 target。
写成代码就是 _target > nums[n - 1] && x >= target _。
如果 x≤nums[n−1],说明 x 在第二段中(或者 nums 只有一段),那么 target 可以在第一段,也可以在第二段。
如果 target 在第一段,那么 x 一定在 target 右边。
如果 target 在第二段,那么 x 必须大于等于 target。
写成代码就是 _target > nums[n - 1] || x >= target _。
根据这两种情况,去判断 x 和 target 的位置关系,从而不断地缩小 target 所在位置的范围,二分找到 target。
细节
二分的范围可以是 [0,n−2]。
这是因为,如果 target 在数组中的位置是 n−1,那么上面分类讨论中的代码,计算结果均为 false。这意味着每次二分更新的都是 left,那么最终答案自然就是 n−1。
普通二分查找
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int searchInsert (int [] nums, int target) { if (nums.length == 0 || nums[0 ] >= target)return 0 ; if (nums[nums.length - 1 ] < target)return nums.length; int l = 0 , r = nums.length -1 ; while (l < r){ int m = (l + r) / 2 ; if (nums[m] < target){ l = m + 1 ; }else { r = m; } } return l; } }
也是二分查找,只是条件不一样了
从矩阵的左下角开始查找,
如果大于target,则行数-1;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix (int [][] matrix, int target) { int i = matrix.length -1 , j = 0 ; while (i >= 0 && j < matrix[0 ].length){ if (matrix[i][j] >target)i--; else if (matrix[i][j] < target)j++; else return true ; } return false ; } }
从上面数组分析,m = 2, 经历遍历后 count = 3,
coumt > 3,说明重复数在左边,
反之 重复数在右边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findDuplicate (int [] nums) { int l = 0 , r = nums.length -1 ; while (l < r){ int m = (l + r)/ 2 ; int count = 0 ; for (int num: nums){ if (num <= m) count++; } if (count > m)r = m; else l = m + 1 ; } return l; } }
当 nums[i]>nums[j] 时: nums[i] 可以接在 nums[j] 之后(此题要求严格递增),此情况下最长上升子序列长度为 dp[j]+1 ;
当 nums[i]<=nums[j] 时: nums[i] 无法接在nums[j]之后,此情况上升子序列不成立,跳过。
上述所有 1. 情况 下计算出的 dp[j]+1 的最大值,为直到 i 的最长上升子序列长度(即 dp[i] )。实现方式为遍历 j 时,每轮执行 dp[i]=max(dp[i],dp[j]+1)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { int res = 0 ; int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(dp,1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++){ if (nums[j] < nums[i])dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); } res = Math.max(dp[i], res ); } return res; } }
双指针 先计算容量长度length
最后移动矮的指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int l = 0 , r = height.length -1 ; int res = 0 ; while (l < r){ int length = r - l; int max = Math.min(height[l], height[r]); res = Math.max(res, max * length ); if (height[l] > height[r])r--; else l++; } return res; } }
这道题其实就算3个数之和为0,边界条件多一点而已,
首先如果num[0] > 0 , 说明后面的数都是> 0的,或者数组长度 < 3直接返回。
然后开始遍历数组,设置头尾指针开始遍历,
如果找到了一个符合条件,存入链表,还要查找是否存在指针的数据,迭代到下个不存在的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); if (nums[0 ] > 0 || nums.length < 3 )return res; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i ++){ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ])continue ; int j = i + 1 , k = nums.length -1 ; while (j < k){ if (nums[j] + nums[i] + nums[k] == 0 ){ res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j],nums[k])); while (j < k && nums[j] == nums[j + 1 ])j++; while (j < k && nums[k] == nums[k - 1 ])k--; j++; k--; }else if (nums[j] + nums[i] + nums[k] < 0 ) j++; else k--; } } return res; } }
先遍历n个元素,使得cur2移动n次
然后再次遍历,让cur1和cur2一起移动
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode p = new ListNode (0 ,head); ListNode cur1 = p; ListNode cur2 = p; while (n != 0 ){ cur2 = cur2.next; n--; } while (cur2.next != null ){ cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } cur1.next = cur1.next.next; return p.next; } }
首先从后面遍历,直至前一个小于后一个元素,说明此处是转换位置记为i
然后又重新从后面遍历,与nums[i]进行比较,如果存在小于元素,说明是该元素与i互换位置,换转位置后,i位置后的元素需重新排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public void nextPermutation (int [] nums) { int i = nums.length - 2 ; while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1 ]){ i--; } if (i >= 0 ){ int j = nums.length - 1 ; while (j >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[j]){ j--; } swap(nums, i , j); } reverse(nums, i + 1 ); } public void swap (int nums[], int i , int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } public void reverse (int [] nums, int i) { int left = i, right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right){ swap(nums, left, right); left++;right--; } } }
75. 颜色分类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public void sortColors (int [] nums) { sort(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } public void sort (int []nums, int l , int r) { if (l >= r)return ; int i = l - 1 ,j = r + 1 ,x = nums[l]; while (i < j){ do i++; while (nums[i] < x); do j--; while (nums[j] > x); if (i < j) swap(nums, i , j); } sort(nums, l, j); sort(nums, j + 1 , r); } public void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } }
使用快慢指针即可,注意循环条件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast!= null && fast.next != null ){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == slow)return true ; } return false ; } }
142. 环形链表 II
首先找到环开始的地方,然后让slow重新开始和fast一起遍历,如果重叠说明是环结束的地方
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { ListNode fast, slow; fast = slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow)break ; } if (fast == null || fast.next == null )return null ; slow = head; while (fast != slow){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } }
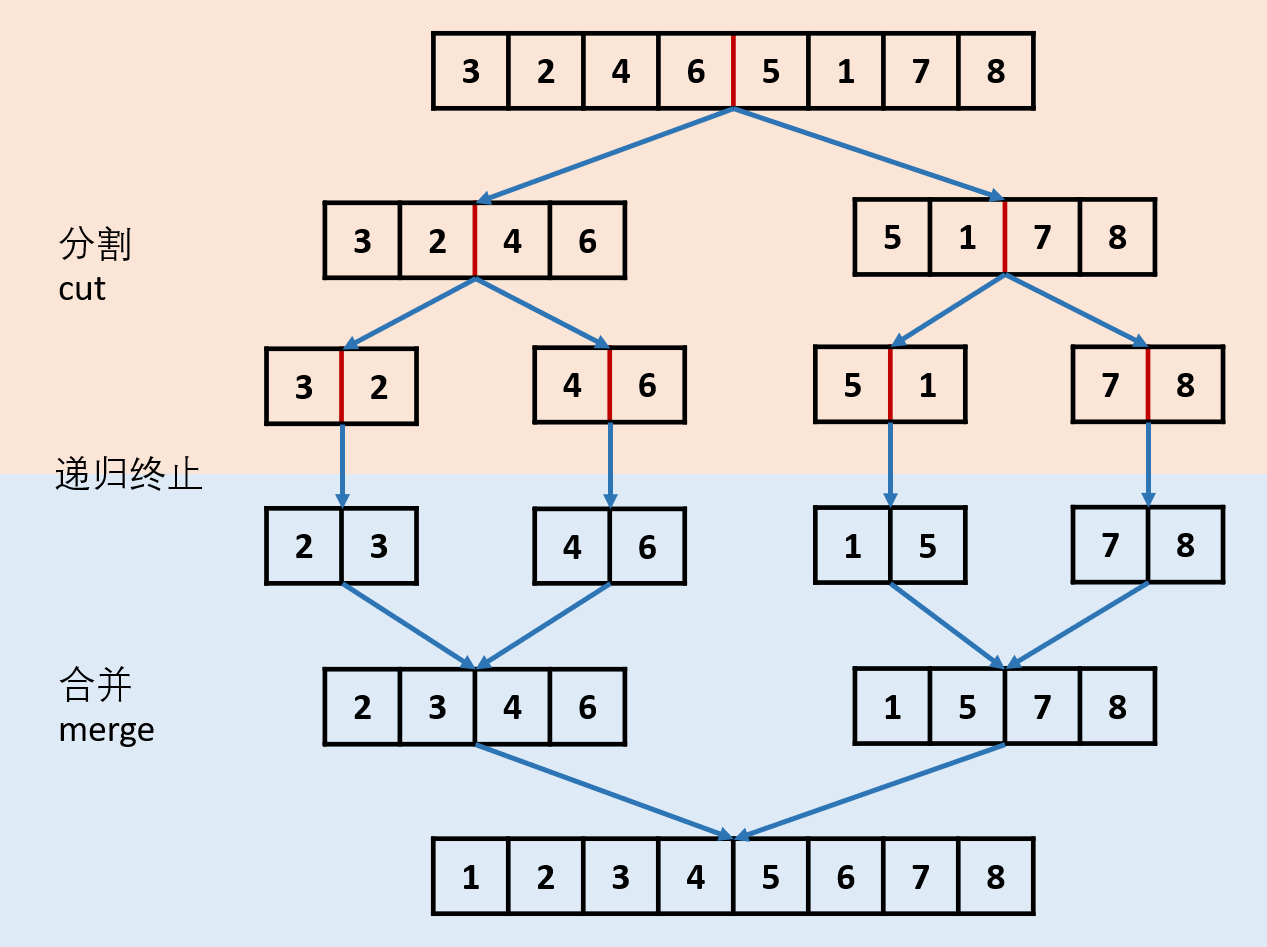
分割 cut 环节: 找到当前链表 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">中点</font>,并从 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">中点</font> 将链表断开(以便在下次递归 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">cut</font> 时,链表片段拥有正确边界);
我们使用 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">fast,slow</font> 快慢双指针法,奇数个节点找到中点,偶数个节点找到中心左边的节点。 找到中点 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">slow</font> 后,执行 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">slow.next = None</font> 将链表切断。 归分割时,输入当前链表左端点 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">head</font> 和中心节点 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">slow</font> 的下一个节点 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">tmp</font>(因为链表是从 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">slow</font> 切断的)。 cut 递归终止条件: 当 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">head.next == None</font> 时,说明只有一个节点了,直接返回此节点。
合并 merge 环节: 将两个排序链表合并,转化为一个排序链表。
双指针法合并,建立辅助 ListNode <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);">h</font> 作为头部 设置两指针 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">left</font>, <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">right</font> 分别指向两链表头部,比较两指针处节点值大小,由小到大加入合并链表头部,指针交替前进,直至添加完两个链表。 返回辅助ListNode <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">h</font> 作为头部的下个节点 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">h.next</font>。 时间复杂度 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">O(l + r)</font>, <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">l, r</font> 分别代表两个链表长度。
当题目输入的 <font style="color:rgba(38, 38, 38, 0.75);background-color:rgb(240, 240, 240);">head == None</font> 时,直接返回 None。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null )return head; ListNode fast = head.next, slow = head; if (fast != null && fast.next !=null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode tmp = slow.next; slow.next = null ; ListNode left = sortList(head); ListNode right = sortList(tmp); ListNode h = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode res = h; while (left != null && right != null ){ if (left.val < right.val){ h.next = left; left = left.next; }else { h.next = right; right = right.next; } h = h.next; } h.next = left != null ? left : right; return res.next; } }
遍历两个链表,如果为空说明到底了,从对面链表开始。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode a = headA; ListNode b = headB; while (a != b){ a = a != null ? a.next : headB; b = b != null ? b.next : headA; } return a; } }
这道题关键是判断这个链表是奇数还是偶数,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } if (fast != null ) slow = slow.next; ListNode l = head; ListNode r = reverse(slow); while (r != null ){ if (r.val != l.val)return false ; r = r.next; l = l.next; } return true ; } public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null , cur = head; while (cur != null ){ ListNode tmp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = tmp; } return pre; } }
双指针遍历,先遍历有数据的,再遍历0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int j = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (nums[i] != 0 ){ nums[j++] = nums[i]; } } for (; j < nums.length; j++){ nums[j] = 0 ; } } }
这题思路是二分查找
设置一个cnt,找到nums中小于等于mid 的元素,如果cnt > mid 说明,cnt里面存在重复元素,否则的话说明在另外一个区间里面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findDuplicate (int [] nums) { int l = 1 , r = nums.length - 1 ; while (l < r){ int m = (l + r )/ 2 ; int cnt = 0 ; for (int num: nums){ if (num <= m)cnt++; } if (cnt > m)r = m; else l = m + 1 ; } return l; } }
设置最大值max,最小值min,左边界l,右边界r
首先从头开始遍历,找到非单调递增区域,
如果存在nums[i] < max ,则可以认为i当前存在于非单调递增区域。所以存起来一直遍历,刷新r的位置。
同理可得:
l为非单调递增区域的最前位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int max = nums[0 ]; int min = nums[n - 1 ]; int l = 0 , r = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (nums[i] < max){ r = i; }else { max = nums[i]; } } for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (nums[i] > min){ l = i; }else { min = nums[i]; } } return r -l + 1 ; } }
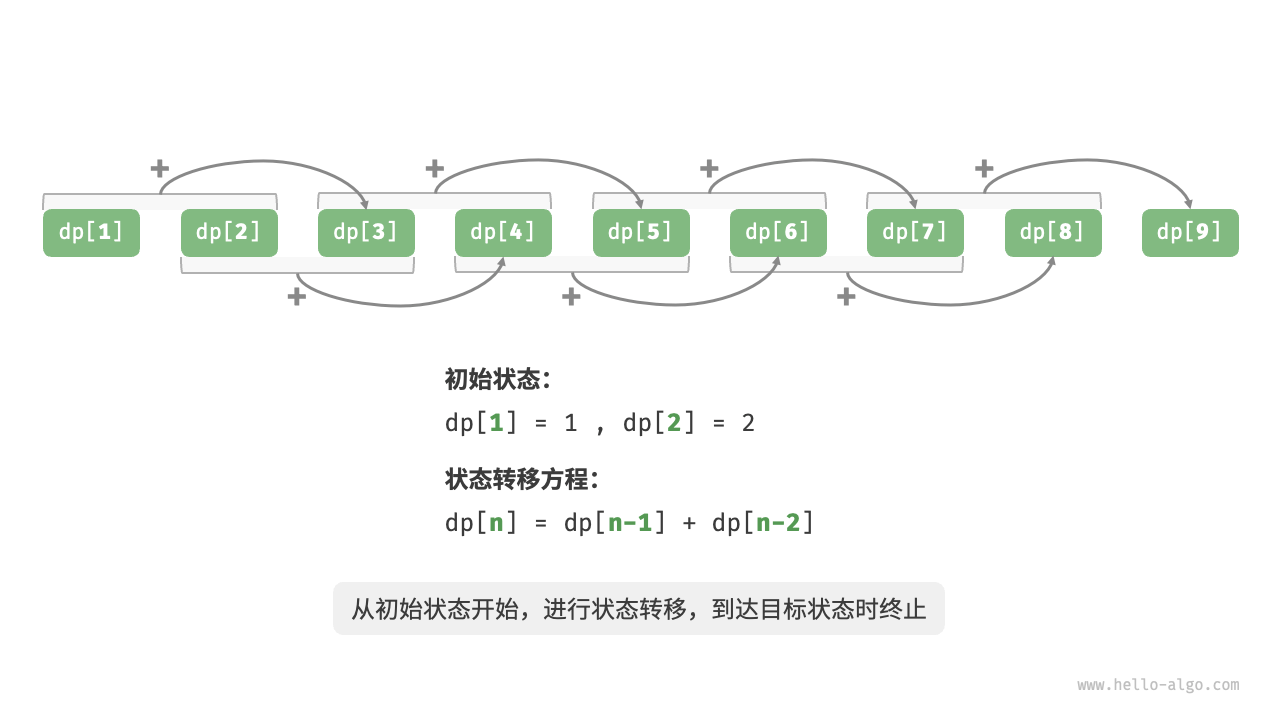
动态规划 动态规划是一种“从底至顶”的方法 :从最小子问题的解开始,迭代地构建更大子问题的解,直至得到原问题的解。
由于动态规划不包含回溯过程,因此只需使用循环迭代实现,无须使用递归。 与回溯算法一样,动态规划也使用“状态”概念来表示问题求解的特定阶段,每个状态都对应一个子问题以及相应的局部最优解。例如,爬楼梯问题的状态定义为当前所在楼梯阶数 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);"> </font><font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">i</font> 。
根据以上内容,我们可以总结出动态规划的常用术语。
将数组 dp 称为 <u><font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp</font></u> 表 , <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i]</font> 表示状态 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">i</font><font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);"> </font>对应子问题的解。 将最小子问题对应的状态(第 1 阶和第 2 阶楼梯)称为 初始状态 。 将递推公式 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i]=dp[i−1]+dp[i−2]</font> 称为 状态转移方程 。
设 d p [ i ] 为爬到第 i 阶累计付出的代价,由于第 i 阶只可能从 i − 1 阶或 i − 2 阶走来,因此 d p [ i ] 只可能等于 d p [ i − 1 ] + c o s t [ i ] 或 d p [ i − 2 ] + c o s t [ i ] 。为了尽可能减少代价,我们应该选择两者中较小的那一个:
<font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i]=min(dp[i−1],dp[i−2])+cost[i]</font>
这便可以引出最优子结构的含义: 原问题的最优解是从子问题的最优解构建得来的 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int n = cost.length - 1 ; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[1 ] = cost[1 ]; dp[0 ] = cost[0 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ]) + cost[i]; } return Math.min(dp[n], dp[n - 1 ]); } }
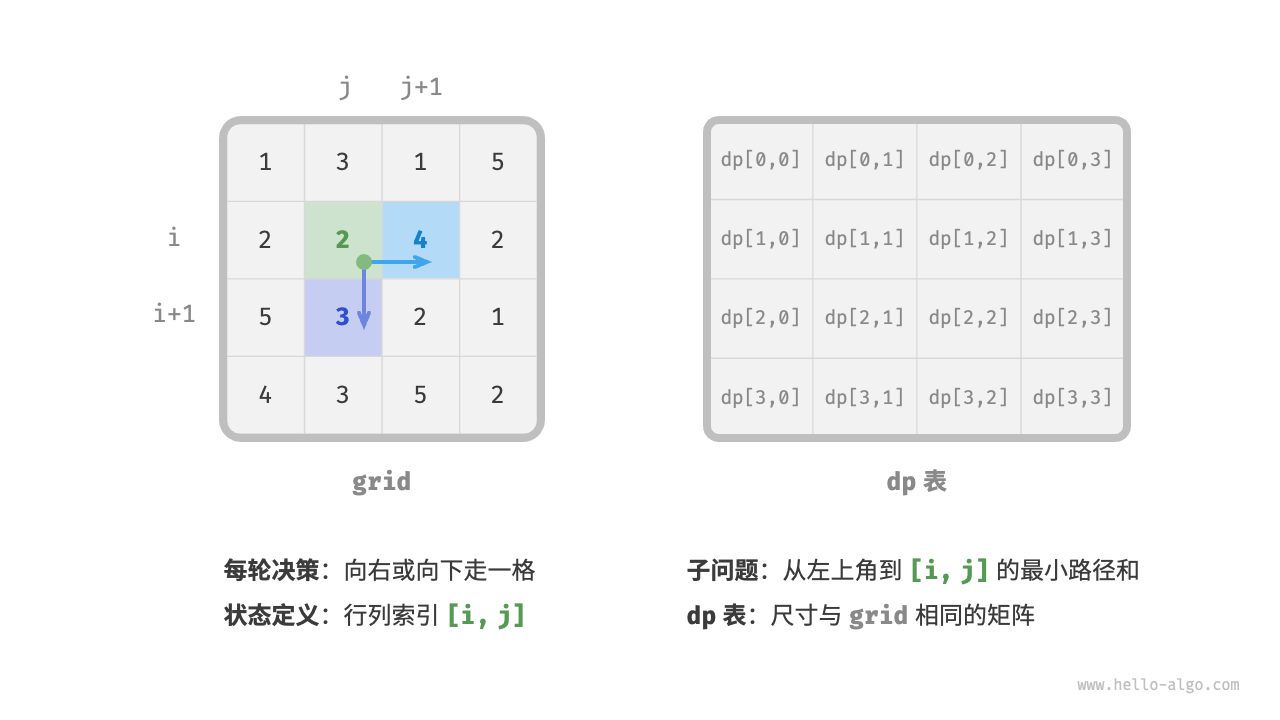
每一次都会让棋子让右或者往下走一步,设当前格子为[i , j], 则往下或往右则变为[i + 1,j]或者[i , j + 1]
然后找出最优解,对于状态 [ i , j ] ,它只能从上边格子 [ i − 1 , j ] 和左边格子 [ i , j − 1 ] 转移而来。因此最优子结构为:到达 [ i , j ] 的最小路径和由 [ i , j − 1 ] 的最小路径和与 [ i − 1 , j ] 的最小路径和中较小的那一个决定。
根据以上分析,可推出图 14-12 所示的状态转移方程:
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
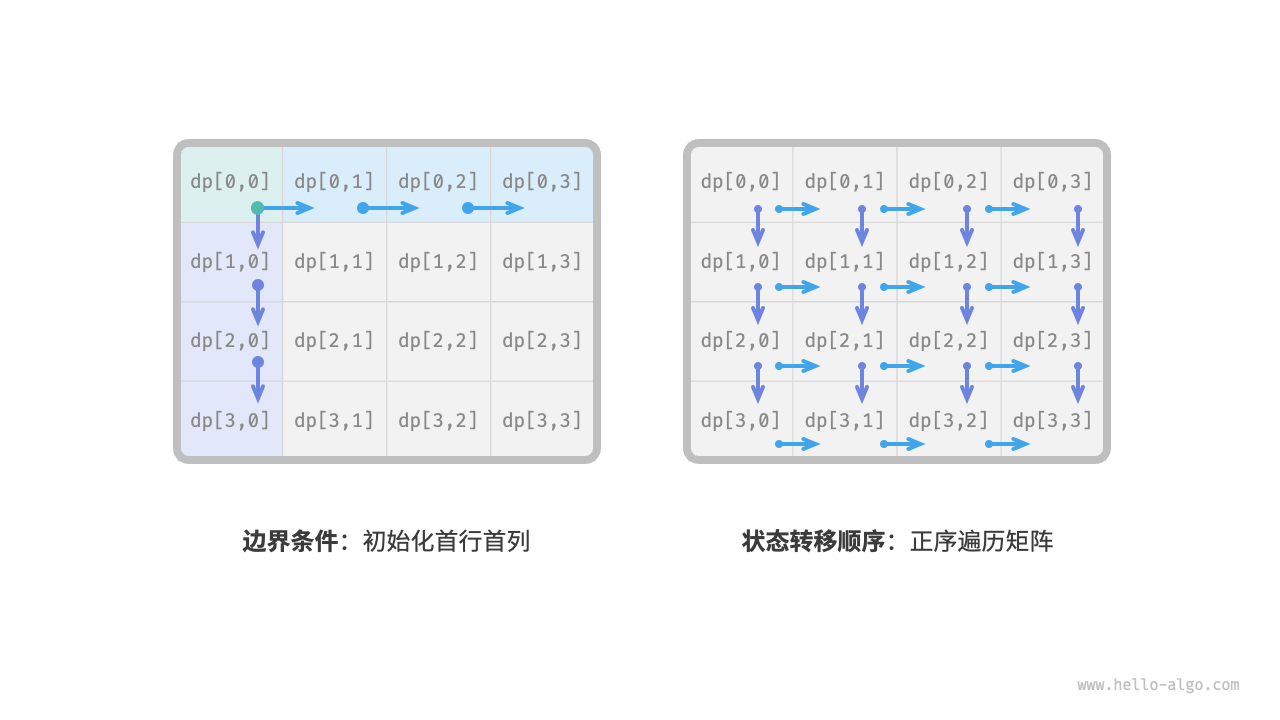
确定边界条件和状态转移顺序
在本题中,处在首行的状态只能从其左边的状态得来,处在首列的状态只能从其上边的状态得来,因此首行 i = 0 和首列 j = 0 是边界条件。
如图 14-13 所示,由于每个格子是由其左方格子和上方格子转移而来,因此我们使用循环来遍历矩阵,外循环遍历各行,内循环遍历各列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int minPathSum (int [][] grid) { int n = grid.length, m = grid[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [n][m]; dp[0 ][0 ] = grid[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++){ dp[0 ][i] = dp[0 ][i - 1 ] + grid[0 ][i]; } for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++){ dp[j][0 ] = dp[j - 1 ][0 ] + grid[j][0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j < m; j++){ dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]) + grid[i][j]; } } return dp[n - 1 ][m - 1 ]; } }
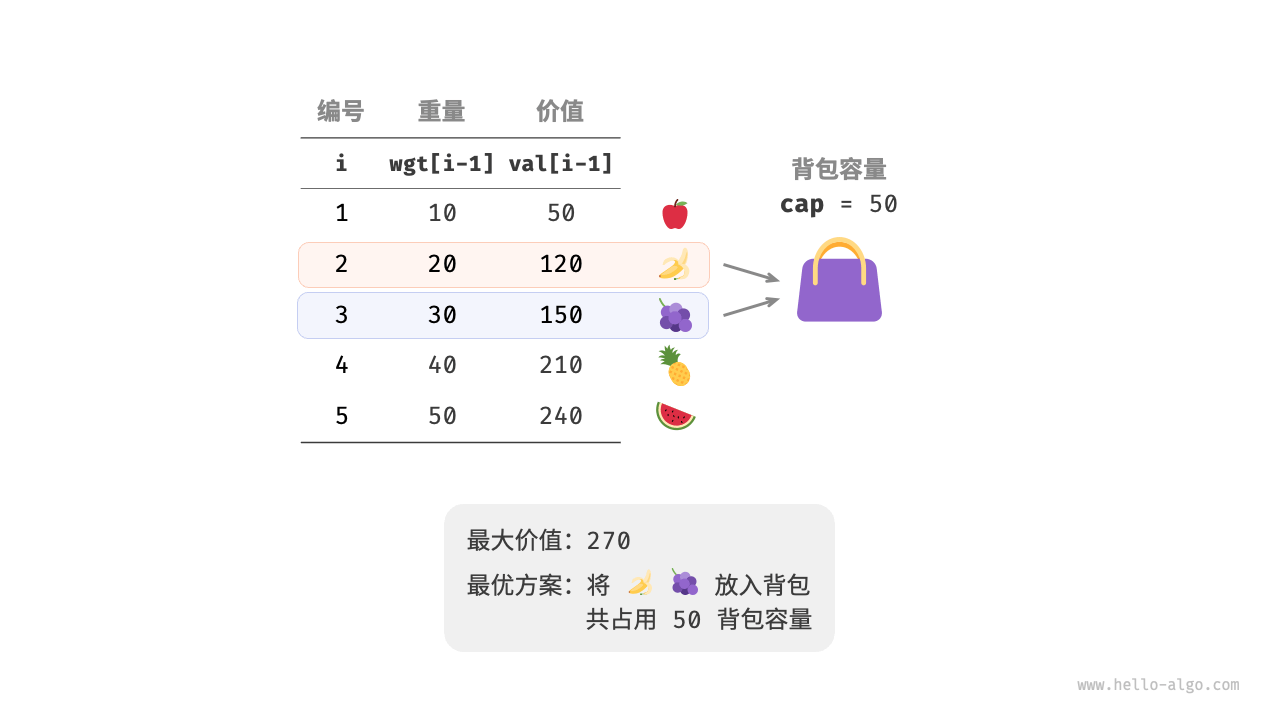
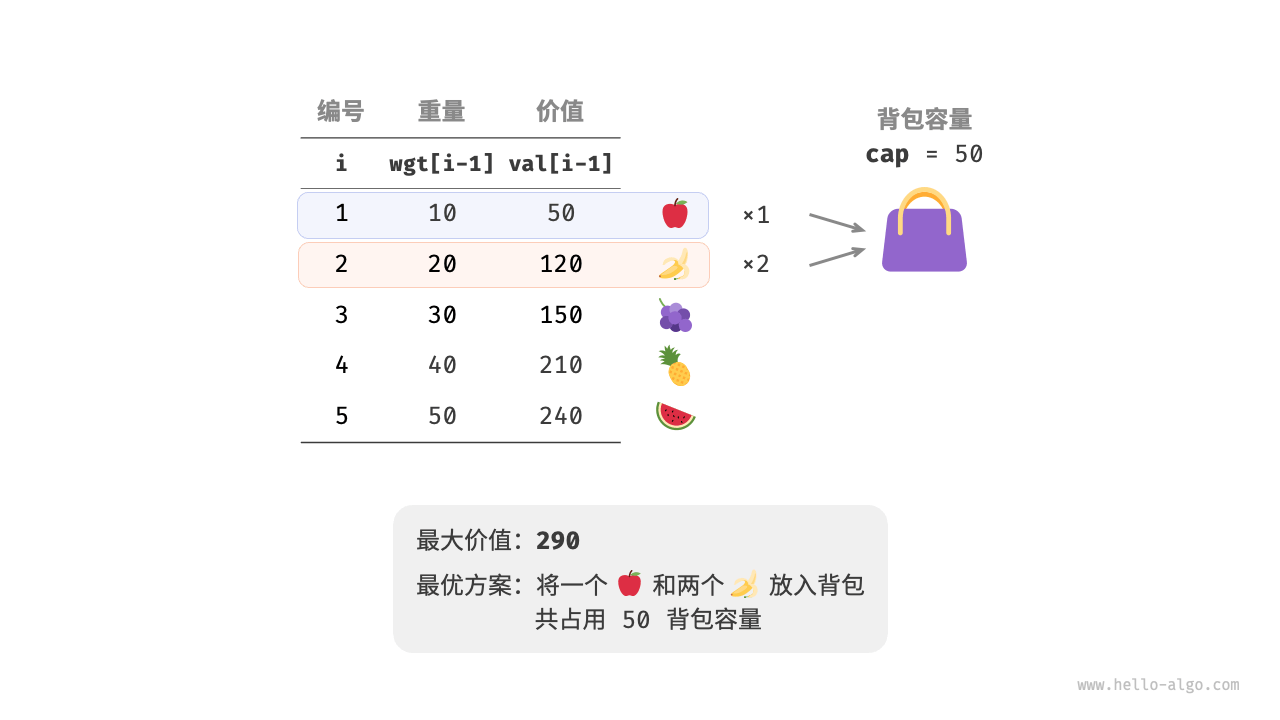
0-1背包
由图所得,物品i对应的重量wgt[i]和价值val[i],每一个物品只能放一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int knapsackDP (int [] wgt, int [] val, int cap) { int n = wgt.length - 1 ; int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][cap + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= cap; j++){ if (wgt[i] > j){ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1 ]; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - wgt[i - 1 ] + val[i - 1 ]); } } } return dp[n][cap]; }
完全背包 和0-1背包不同的是,它的物品可以放多次,在完全背包问题的规定下,状态 [ i , c ] 的变化分为两种情况。
不放入物品 ****i :与 0-1 背包问题相同,转移至 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">[i−1,c] </font>。 放入物品 ****i :与 0-1 背包问题不同,转移至 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">[i,c−wgt[i−1]] 。</font>
从而状态转移方程变为:
<font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i,c]=max(dp[i−1,c],dp[i,c−wgt[i−1]]+val[i−1])</font>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int unboundedKnapsackDP (int [] wgt, int [] val, int cap) { int n = wgt.length; int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][cap + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int c = 1 ; c <= cap; c++) { if (wgt[i - 1 ] > c) { dp[i][c] = dp[i - 1 ][c]; } else { dp[i][c] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][c], dp[i][c - wgt[i - 1 ]] + val[i - 1 ]); } } } return dp[n][cap]; }
看作完全背包的另一种思路,但求得是最小值
<font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i,a]=min(dp[i−1,a],dp[i,a−coins[i−1]]+1)</font>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 int coinChangeDP (int [] coins, int amt) { int n = coins.length; int MAX = amt + 1 ; int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][amt + 1 ]; for (int a = 1 ; a <= amt; a++) { dp[0 ][a] = MAX; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int a = 1 ; a <= amt; a++) { if (coins[i - 1 ] > a) { dp[i][a] = dp[i - 1 ][a]; } else { dp[i][a] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][a], dp[i][a - coins[i - 1 ]] + 1 ); } } } return dp[n][amt] != MAX ? dp[n][amt] : -1 ; }
本题目标是求组合数量,因此子问题变为: 前 i 种硬币能够凑出金额 a 的组合数量 。而 d p 表仍然是尺寸为 ( n + 1 ) × ( a m t + 1 ) 的二维矩阵。
当前状态的组合数量等于不选当前硬币与选当前硬币这两种决策的组合数量之和。状态转移方程为:
<font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i,a]=dp[i−1,a]+dp[i,a−coins[i−1]]</font>
当目标金额为 0 时,无须选择任何硬币即可凑出目标金额,因此应将首列所有 dp[i,0] 都初始化为 1 。当无硬币时,无法凑出任何 >0 的目标金额,因此首行所有 dp[0,a] 都等于 0 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 int coinChangeIIDP (int [] coins, int amt) { int n = coins.length; int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][amt + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int a = 1 ; a <= amt; a++) { if (coins[i - 1 ] > a) { dp[i][a] = dp[i - 1 ][a]; } else { dp[i][a] = dp[i - 1 ][a] + dp[i][a - coins[i - 1 ]]; } } } return dp[n][amt]; }
输入两个字符串 s 和 t ,返回将 s 转换为 t 所需的最少编辑步数。
你可以在一个字符串中进行三种编辑操作:插入一个字符、删除一个字符、将字符替换为任意一个字符。
若 s[n−1] 和 t[m−1] 相同,我们可以跳过它们,直接考虑 s[n−2] 和 t[m−2] 。 若 s[n−1] 和 t[m−1] 不同,我们需要对 s 进行一次编辑(插入、删除、替换),使得两字符串尾部的字符相同,从而可以跳过它们,考虑规模更小的问题。
不同的操作:
在 s[i−1] 之后添加 t[j−1] ,则剩余子问题 dp[i,j−1] 。 删除 s [ i − 1 ] ,则剩余子问题 d p [ i − 1 , j ] 。 将 s[i−1] 替换为 t[j−1] ,则剩余子问题 dp[i−1,j−1] 。
可得最优子结构:dp[i,j] 的最少编辑步数等于 dp[i,j−1]、dp[i−1,j]、dp[i−1,j−1] 三者中的最少编辑步数,再加上本次的编辑步数 1 。对应的状态转移方程为:
<font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i,j]=min(dp[i,j−1],dp[i−1,j],dp[i−1,j−1])+1</font>
确定边界条件和状态转移顺序
当两字符串都为空时,编辑步数为 0 ,即 dp[0,0]=0 。 当 s 为空但 t 不为空时 ,最少编辑步数等于 t 的长度,即首行 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);"> dp[0,j]=j</font> 。 当 s 不为空但 t 为空时 ,最少编辑步数等于 s 的长度,即首列 <font style="color:rgb(29, 29, 32);">dp[i,0]=i</font> 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int n = word1.length(), m = word2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][m + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ dp[0 ][i] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j<= m; j++){ if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]),dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ])+ 1 ; } } } return dp[n][m]; } }
前一个和后一个比较,小了+1,大了重新排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findLengthOfLCIS (int [] nums) { if (nums.length < 1 )return nums.length; int count = 1 ; int ans = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++){ if (nums[i + 1 ] > nums[i]){ count++; }else { count = 1 ; } ans = count > ans ? count : ans; } return ans; } }
跟背包差不多
如果是边界为0的话,则步数 + 1,不是的话等于上面的值+左边的值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m ;i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++){ if (i == 0 || j == 0 ){ dp[i][j] = 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j] + dp[i][j - 1 ]; } } } return dp[m - 1 ][n - 1 ]; } }
**
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; int min = prices[0 ]; int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ res = Math.max(res, prices[i] - min); min = Math.min(min, prices[i]); } return res; } }
如果i > c 说明没法跳跃了或者c = 0,返回false
计算跳跃位置 从i 跳跃到 i + nums[i]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int c = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > c)return false ; c = Math.max(c, i + nums[i]); } return true ; } }
这道题应该是贪心做法比较好,但这里举出dp形式的
注意 i + j < n;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { int []dp = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(dp,Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= nums[i] && i + j < nums.length; j++){ dp[i + j] = Math.min(dp[i + j], dp[i] + 1 ); } } return dp[nums.length - 1 ]; } }
跳格偷钱,如果拿了i 家的钱,下一家就必须是i + 2,因此有
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i - 1])。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[1 ] = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i < n + 1 ; i++){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ],dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i - 1 ]); } return dp[n]; } }
和上一题相比这道题是使用树节点,这次抢了就要跳过下家,去下下家
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { HashMap<TreeNode, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); public int rob (TreeNode root) { if (root == null )return 0 ; if (map.containsKey(root)){ return map.get(root); } int d = root.val + (root.left == null ? 0 : rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right)) + (root.right == null ? 0 : rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right)); int nd = rob(root.left) + rob(root.right); int res = Math.max(d, nd); map.put(root, res); return res; } }
想卖出最大利润,则需要计算股价最小值,使用min统计,由于只能进行一次买卖,所以使用res维护最大值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; int min = prices[0 ]; int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ res = Math.max(res, prices[i] - min); min = Math.min(min, prices[i]); } return res; } } class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [n][2 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], -prices[i]); } return dp[n - 1 ][0 ]; } }
这道题比上一道多了一个冷却时间,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int n = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [n + 2 ][2 ]; dp[1 ][1 ] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ dp[i + 2 ][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ][0 ],dp[i + 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i + 2 ][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ][1 ],dp[i][0 ] - prices[i]); } return dp[n + 1 ][0 ]; } }
 s
s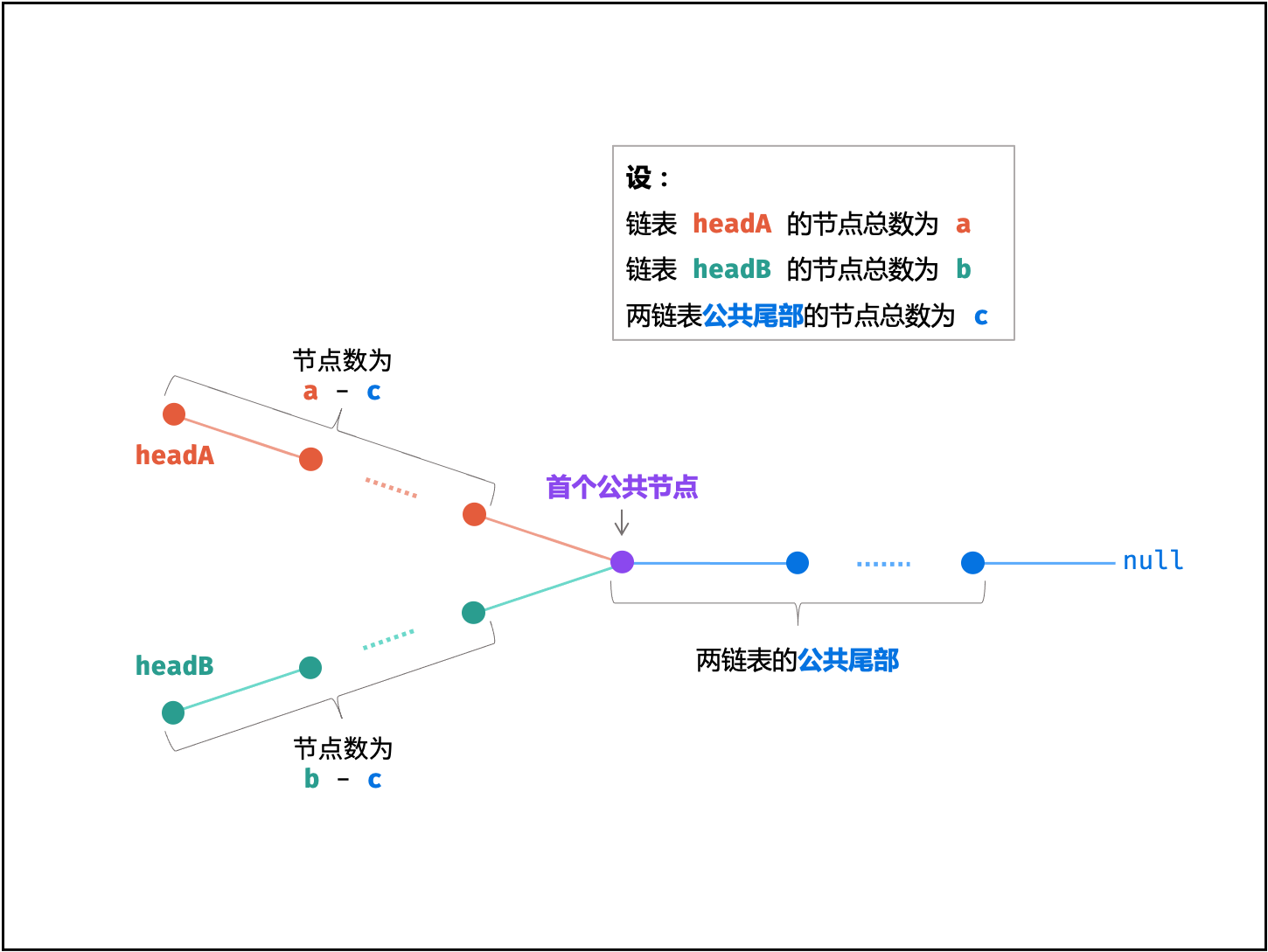
 与回溯算法一样,动态规划也使用“状态”概念来表示问题求解的特定阶段,每个状态都对应一个子问题以及相应的局部最优解。例如,爬楼梯问题的状态定义为当前所在楼梯阶数
与回溯算法一样,动态规划也使用“状态”概念来表示问题求解的特定阶段,每个状态都对应一个子问题以及相应的局部最优解。例如,爬楼梯问题的状态定义为当前所在楼梯阶数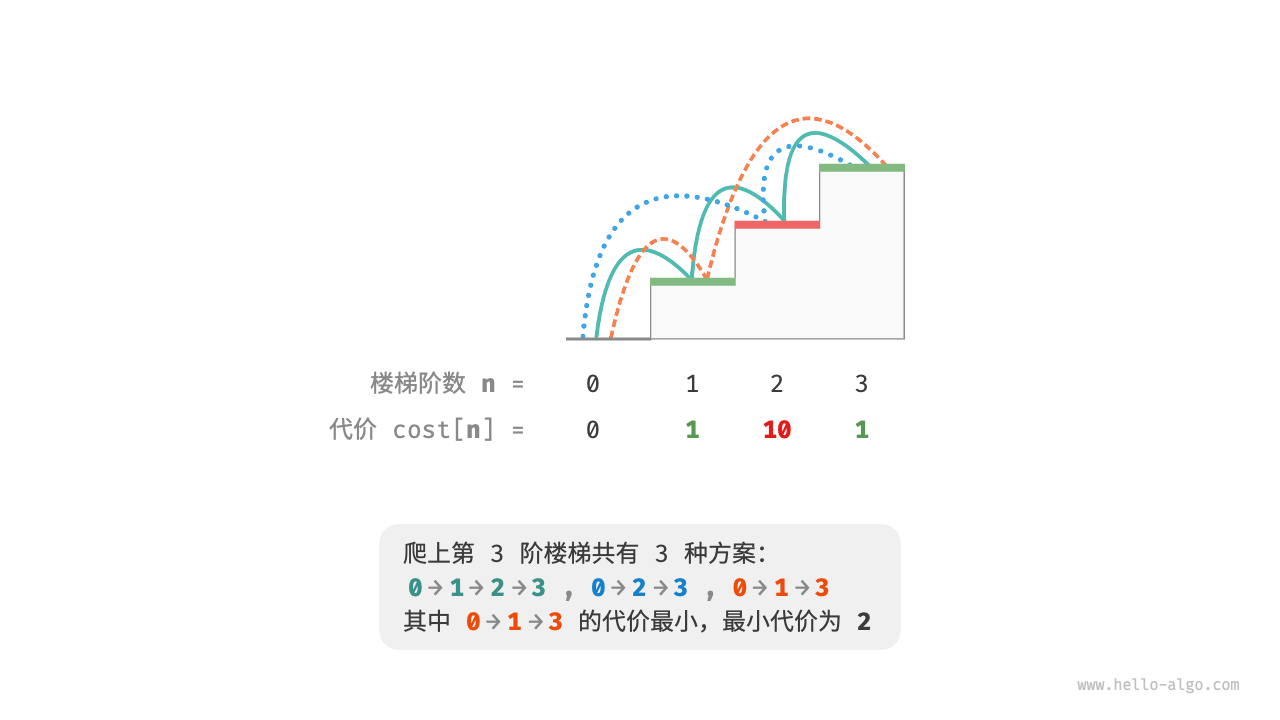
 在完全背包问题的规定下,状态 [i,c] 的变化分为两种情况。
在完全背包问题的规定下,状态 [i,c] 的变化分为两种情况。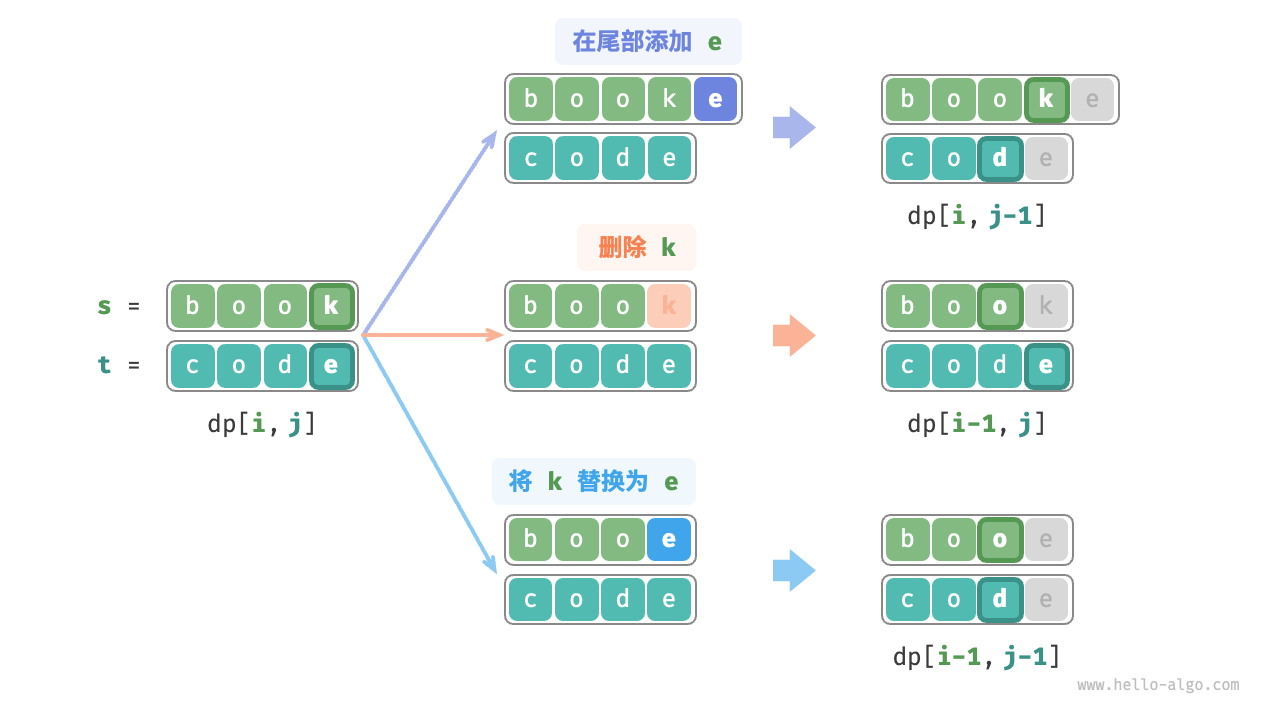 可得最优子结构:dp[i,j] 的最少编辑步数等于 dp[i,j−1]、dp[i−1,j]、dp[i−1,j−1] 三者中的最少编辑步数,再加上本次的编辑步数 1 。对应的状态转移方程为:
可得最优子结构:dp[i,j] 的最少编辑步数等于 dp[i,j−1]、dp[i−1,j]、dp[i−1,j−1] 三者中的最少编辑步数,再加上本次的编辑步数 1 。对应的状态转移方程为: